Jesuit Order All Roads Lead to the Black Pope
The Jesuit Vatican New World Order
“Why would the Jesuits use their implacable enemy, the Jews, to further their designs for world dominion? The Jesuits never do anything out in the open where they can be exposed. If they are recognized as the culprits, they will be blamed and suffer the consequences, but if they can use someone else as the cause of the worlds problems, especially an enemy they can destroy in the process, then they have simultaneously accomplished two of their objectives. The Jewish people are the perfect scapegoat. Since the Rothschilds are Jesuit agents operating under a Jewish cover, using them [i.e., the Rothschilds] in forming the Illuminati back in 1776 effectively throws the onus of this conspiracy on the Jews. The Rothschilds are certainly not the only Jesuit agents that operate under a Jewish front.”
– The following sources [Ed. Note: Bill Hughes lists a number of books in later paragraphs] indicate that [Jesuit] Adam Weishaupt and the Rothschilds were the brains and the wealth behind the French Revolution.
~ Bill Hughes (From his book The Enemy Unmasked)- – – – – – -The Jesuit Order is an almost 500-year old covert operations, geo-political, male-only organization, structured as a secret military operation: demanding secret oaths and complete obedience to each direct superior, which is ultimately the Superior General (often nicknamed as theBlack Pope, since he dresses in black and ‘stands in the shadow’ of the white Pope).
The “Society of Jesus” – as they are officially known – was originally used by the Vatican to counter the various Reformation movements in Europe, to which the Vatican lost much of its religious and political power. Absolute-temporal-ruling power has always been the Vatican institution’s primary objective.
The Jesuit Order is since 1814 in complete control of the – obscenely wealthy– Vatican institution (and its Catholic clergy hierarchy) and presently also controls various other organizations together with the Military Order of Malta, such as:osingworlddeception.blogspot.com]

“My history of the Jesuits is not eloquently written, but it is supported by unquestionable authorities, [and] is very particular and very horrible. Their [the Jesuit Order’s] restoration [in 1814 by Pope Pius VII] is indeed a step toward darkness, cruelty, despotism, [and] death. … I do not like the appearance of the Jesuits. If ever there was a body of men who merited eternal damnation on earth and in hell, it is this Society of [Ignatius de] Loyola.”
– John Adams (1735-1826; 2nd President of the United States)
“The Jesuits…are a secret society – a sort of Masonic order – with superadded features of revolting odiousness, and a thousand times more dangerous.”
– Samuel Morse (1791-1872; American inventor of the telegraph; author of the book Foreign Conspiracy Against the Liberties of the United States)
“Above all I have learned from the Jesuits. And so did Lenin too, as far as I recall. The world has never known anything quite so splendid as the hierarchical structure of the [Roman] Catholic Church. There were quite a few things I simply appropriated from the Jesuits for the use of the [Nazi] Party.
– Adolph Hitler (1889-1945; Nazi leader and chancellor of Germany from 1933-1945)
((Ed. Comment: What follows is a similar quotation of Hitler taken from Edmond Paris’ book The Vatican Against Europe.))
“I have learnt most of all from the Jesuit Order. So far, there has been nothing more imposing on earth than the hierarchical organization of the Catholic Church. A good part of that organization I have transported direct to my own party. The Catholic Church must be held up as an example. I will tell you a secret. I am founding an order. In Himmler (who would become head of the Nazi party) I see our Ignatius de Loyola (Jesuit founder).”
– Adolph Hitler
“The Jesuits are a MILITARY organization, not a religious order. Their chief is a general of an army, not the mere father abbot of a monastery. And the aim of this organization is power – power in its most despotic exercise – absolute power, universal power, power to control the world by the volition of a single man. Jesuitism is the most absolute of despotisms – and at the same time the greatest and most enormous of abuses.”
– Napoleon I (i.e., Napoleon Bonaparte; 1769-1821; emperor of the French)
“It is my opinion that if the liberties of this country – the United States of America – are destroyed, it will be by the subtlety of the Roman Catholic Jesuit priests, for they are the most crafty, dangerous enemies to civil and religious liberty. They have instigated MOST of the wars of Europe.”
– Marquis de LaFayette (1757-1834; French statesman and general. He served in the American Continental Army under the command of General George Washington during the American Revolutionary War.)
“Alas, I knew they [i.e., the Jesuits] would poison me; but I did not expect to die in so slow and cruel a manner.” (1774)
– Pope Clement XIV (Who had “forever” abolished the Jesuit Order in 1773)
“The war [i.e., the American Civil War of 1861-1865] would never have been possible without the sinister influence of the Jesuits.”
– Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865; 16th President of the United States)The public is practically unaware of the overwhelming responsibility carried by the Vatican and its Jesuits in the starting of the two world wars – a situation which may be explained in part by the gigantic finances at the disposition of the Vatican and its Jesuits, giving them power in so many spheres, especially since the last conflict.”
– Edmond Paris (Author of the book The Secret History of the Jesuits)
“…The Roman Inquisition…had been administered since 1542 by the Jesuits.”
– F. Tupper Saussy (Author of the book Rulers of Evil)
“It is impossible to read Elizabethan history [i.e., the history surrounding Queen Elizabeth I of England; queen: 1558-1603] except in the context of an army of Jesuits, masters of deceit, treachery, treason, infiltration, subversion, assassination, insurrection, civil war and coercion, plotting for the good of the papacy, and the defeat of all the Pope’s foes anywhere in the world.” (1987)
– J.E.C. Shepherd (Canadian historian)
“Between 1555 and 1931 the Society of Jesus [i.e., the Jesuit Order] was expelled from at least 83 countries, city states and cities, for engaging in political intrigue and subversion plots against the welfare of the State, according to the records of a Jesuit priest of repute [Thomas J. Campbell]. …Practically every instance of expulsion was for political intrigue, political infiltration, political subversion, and inciting to political insurrection.” (1987)
– J.E.C. Shepherd (Canadian historian)
(7) “The [German General Reinhard] Gehlen Org, the German Intelligence Agency run by [Knight of Malta] Reinhard Gehlen, was even more powerful than the Merk net. The Org superseded even the Nazi SS… In fact, Gehlen’s organization is largely credited for giving rise to the CIA…to shield Gehlen and the entire German Intelligence network from harm’s way. Gehlen was a ranking official in the Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), which maintained inconceivable financial support and political influence… Somehow I wasn’t surprised to learn that financial motives…were at the heart of the SMOM and the Nazi-American alliance… Soon after the war, OSS [i.e., Office of Strategic Services – the forerunner to the CIA] found the extensive documentation of a meeting…between representatives of the [Nazi] SS…and firms like…I.G. Farben… [The] world’s masses knew nothing about the partnership, formed between John D. Rockefeller’s Standard Oil Company, Germany’s I.G. Farben, and Hitler’s Third Reich. The ‘pirates of Wall Street’, Allen and John Foster Dulles, of the law firm Sullivan & Cromwell, had secretly negotiated the alliance. It was not known to allied airmen, flying bombing missions over Germany, why the I.G. Farben plants, where Hitler’s munitions were made, were exempted from attack. Likewise, when the I.G. Farben – Rockefeller Consortium used concentration camp victims as slaves to build and run their factories it never made the news… Nor was it heralded that this same TEAM patented and sold the gas that the Nazis used in the concentration camps to send millions to their graves. Recent headlines have asked to know where the Nazi gold went. Historians only recently recorded that the Rockefeller’s Chase Bank [manned by a high Knight of Malta, Joseph J. Larkin] was among the largest recipients…”
– Dr. Leonard Horowitz, author of the book Emerging Viruses: AIDS and Ebola
“[Wherever] a totalitarian movement erupts, whether Communist or Nazi [Fascist], a Jesuit can be found in the role of ‘adviser’ or leader; in Cuba [it was] [Jesuit-trained] Castro’s ‘Father’ Armando Llorente…”
– Emanuel M. Josephson (American physician and historian)
“[The Jesuits] are the deadly enemies of civil and religious liberty.”
– R. W. Thompson (Ex-Secretary, American Navy)
“The principles of socialism or communism…governed all the [Jesuit-run] Reductions [in Paraguay].”
– R. W. Thompson, Ex-Secretary, American Navy
“The whole frightful responsibility for this terrible Thirty Years’ War [1618-1648] must rest upon the [Holy Roman] Emperor Ferdinand II, and his teachers, rulers, and bosom friends – the Sons of Loyola [i.e., the Jesuit Order].”
– Theodor Griesinger (German historian; 1873)
“The Jesuit Order at last reached the pinnacle of its power and prestige in the early eighteenth century [i.e., the early 1700s]. It had become more influential and more wealthy than any other organization in the world. It held a position in world affairs that no oath-bound group of men has ever held before or since… ‘Nearly all the Kings and Sovereigns of Europe had only Jesuits as directors of their consciences [i.e., as confessor-priests], so that the whole of Europe appeared to be governed by Jesuits only.’” (1927; using a short quote by Jesuit Cordara)
– Boyd Barrett (Ex-Jesuit)
“If you trace up Masonry, through all its Orders, till you come to the grand tip-top head Mason of the World, you will discover that the dread individual and the Chief of the Society of Jesus [i.e., the Superior General of the Jesuit Order] are one and the same person.”
– James Parton (American historian)
“In Roman Catholic circles it is well known that the Black Pope is the term used for the [Superior] General of the Jesuits. As the Pope is always robed in white, and the [Jesuit Superior] General in black, the contrast is obvious. But those Romanists who do not greatly love the Jesuits, and their number is not limited, use the term as indicating that the Black Pope rules the White Pope…even while the former [i.e., the Black Pope] is obligated to make, at least, a show of submission to the latter.” (1896)
– M.F. Cusack (Ex-nun of Kenmore; author of the book The Black Pope)
“…The Jesuits are the only religious order in the Church of Rome…which has lain under the ban of the [‘White’] Pope, or which has been expelled from any country because of its interference in politics. Hence we may expect to find that to obtain political power forms a main feature in the plans of the Society [of Jesus – i.e., the Jesuit Order].” (1896)
– M.F. Cusack
“All these things cause the Father-General [of the Jesuits] to be feared by the Pope and sovereigns… A sovereign who is not their [the Jesuits’] friend will sooner or later experience their vengeance.” (1852)
– Luigi Desanctis (Official Censor of the Inquisition)
“The Society of Jesus [i.e., the Jesuit Order] is the enemy of man. The whole human race should unite for its overthrow. …For there is no alternative between its total extirpation, and the absolute corruption and degradation of mankind.”
– Robert J. Breckinridge (author)
“The Jesuits…are simply the Romish army for the earthly sovereignty of the world in the future, with the Pontiff of Rome for emperor…that’s their ideal. …It is simple lust of power, of filthy earthly gain, of domination – something like a universal serfdom with them [i.e., the Jesuits] as masters – that’s all they stand for. They don’t even believe in God perhaps.”
– Fyodor Dostoyevsky (1821-1881; famous Russian novelist)
“I [Roman Catholic Bishop Palafox] found almost all the wealth…and all the treasures of the Province of America in the hands of the Jesuits… ((Ed. Comment: I assume the Bishop is talking specifically about SOUTH America.))
All this property and all these considerable revenues which might make a sovereign powerful, serve no other purpose than to maintain ten [Jesuit] colleges… To this may be added the extraordinary skill with which they [the Jesuits] make use of and increase their super-abundant wealth. They maintain public warehouses, cattle fairs, butcher-stalls, and shops… They lend out their money for usury, and thus cause the greatest loss and injury to others.”
– Roman Catholic Bishop Palafox (from a letter of his in 1647)
“For the Vatican [Ed. Comment: Even then controlled by the Black Pope and his Jesuit Order] condemned the Declaration of Independence as ‘wickedness’…and called the Constitution of the United States ‘a Satanic document’.”
– Avro Manhatten (author; from his book The Dollar and the Vatican)
“The [Jesuit Superior] General is at the head of this black and mute militia, which thinks, wills, acts, obeys – [as] the passive instrument of his designs. Their whole life must have but one aim – the advancement of the [Jesuit] Order to which they are attached.” (1912)
– Jeremiah J. Crowley (Irishman; ex-priest in the Roman Catholic Church; author of the book Romanism: Menace to the Nation)
“Never before in the course of the world’s history had such a Society [i.e., the Jesuit Order] appeared. The old Roman Senate itself did not lay schemes for world domination with greater certainty of success.” (1800)
– Friedrich von Hardenberg (German philosopher)
“[Jesuit-trained Illuminist Adam] Weishaupt and his fellow Jesuits cut off the income to the Vatican by launching and leading the French Revolution; by directing Napoleon’s conquest of Catholic Europe; [and] …by eventually having Napoleon throw Pope Pius VII in jail at Avignon until he agreed, as the price for his release, to reestablish the Jesuit Order. This Jesuit war on the Vatican was terminated by the Congress of Vienna and by the secret, 1822 Treaty of Verona.”
– Emanuel M. Josephson (American physician and historian)
“Why would the Jesuits use their implacable enemy, the Jews, to further their designs for world dominion? The Jesuits never do anything out in the open where they can be exposed. If they are recognized as the culprits, they will be blamed and suffer the consequences, but if they can use someone else as the ‘cause of the world’s problems’, especially an enemy they can destroy in the process, then they have simultaneously accomplished two of their objectives. The Jewish people are the perfect scapegoat. Since the Rothschilds are Jesuit agents operating under a Jewish cover, using them [i.e., the Rothschilds] in forming the Illuminati back in 1776 effectively throws the onus of this conspiracy on the Jews. The Rothschilds are certainly not the only Jesuit agents that operate under a Jewish front.
“History books will tell us that the French Revolution first began in 1787 or 1789, depending on which book you read. However, it was actually planned by [Jesuit] Dr. Adam Weishaupt and the House of Rothschild almost 20 years before the Revolution took place.”
– William Sutton (Author of The New Age Movement and The Illuminati 666)
“They [i.e., the Jesuits] have so constantly mixed themselves up in court and state intrigues that they must, in justice, be reproached with striving after world dominion. They cost kings their lives, not on the scaffold, but by assassination, and equally hurtful as the society of Illuminati; they were the foremost among the crowd, at all events, who applauded the murder scenes in Paris [during the French Revolution].”
Hector Macpherson (Author of the book The Jesuits in History)
“[Jesuit Adam] Weishaupt established the [modern version of the] Illuminati specifically to be a front organization behind which the Jesuits could hide. After being [formally] abolished by [Pope] Clement XIV in 1773, the Jesuits used the Illuminati and other organizations to carry out their operations. Thus, the front organizations would be blamed for the trouble caused by the Jesuits.”
– Bill Hughes (Author of The Secret Terrorists and The Enemy Unmasked)
The following sources [Ed. Note: Bill Hughes lists a number of books in later paragraphs] indicate that [Jesuit] Adam Weishaupt and the Rothschilds were the brains and the wealth behind the French Revolution.”
– Bill Hughes (From his book The Enemy Unmasked)
“It is my opinion that if the liberties of this country – the United States of America – are destroyed, it will be by thesubtlety of the Roman Catholic Jesuit priests, for they are the most crafty, dangerous enemies to civil and religious liberty. They have instigated most of the wars of Europe.”
George Washington
– “Shall we not have regular swarms of them here, in as many disguises as only a king of the gypsies can assume, dressed as painters, publishers, writers, and schoolmasters? If ever there was a body of men who merited eternal damnation on Earth and in Hell it is this Society of Loyola’s.”
President John Adams
Achievements of the Jesuit Order
— Make lending of money on interest a noble occupation.
— Place Jews in positions where fault or blame can be placed in the future.
— Exterminate heretic leaders and key opponents.
— Arrange for puppet leaders like Hitler, Mao, Stalin to extend the inquisition.
— Arrange for the slaughter of the Indigenous infidels.
— Institutionalize the Corporation to compete with the individual.
— Establishment of the Central Government for the United States
— Establish the United States Federal Reserve Bank
— Control and facilitate the “Secret Societies” .
— Centralize inner power by controlling the nations Secret Services
— Fabricate conflicts such as the Cold War and Terrorism
— Create artificial events such as 9/11 to manipulate populations
— Control thinking by controlling Educational, History, Media
– Maintain a conscript army through economic repression and inquisition.
–Manage the health of the populous.
Jesuit Assassinations
Many are those who have dared to stand against the great Jesuit General and the Great Jesuit cause. But, where are they now? What have they achieved except their own ruination and that of their own lands? How can theunworthy heretic think they can oppose the great Jesuit Order and Organization? The Jesuit brotherhood will destroy the heretics and the indigenous peoples and their wrong beliefs taking from them everything and leavingthem stunned, shocked and dismayed. Most heretics will not live past the coming inquisitions nor do they deserve to.
All successful revolutionary activity is started from the top by leadership. Therefore potential leaders must be assassinated as soon as there is the slightest indication of their potential to undermine the Jesuit strategy.
Righteous Jesuit Assassinations
Pope Clement XIV – Suppressed the Jesuit order in 1773 and was assassinated.
JFK – Dared to resist the authority of the Jesuit General and was assassinated.
Abraham Lincoln – Resisted the Jesuits after the Civil War and was assassinated.
Benito Pablo Juarez – Purged Mexico of the Jesuit influence and was assassinated.
Malcolm X – Assassinated for efforts to root out the Masonic influence over the Black Muslims.
Louis T. McFadden – Assassinated for promoting the end of the Federal Reserve.
Che Guevara – Assassinated for resisting the Jesuit subjugation of South America.
General Lafayette, 1799 Aide to Washington Romanism: A Menace to the Nation
 |
 |
| 265th Pope Joseph Ratzinger and 30th Jesuit General Adolfo Nicolás. | 35th Jesuit general congregation at the Vatican in 2008 |
“The Jesuits have no women. They have no love of a woman. Because to have a wife, to have a woman, means you have an allegiance to your wife and family, and you cannot obey the General. That’s why they will NEVER be married, and that’s one of the great KEYS to their success.”– Eric Jon Phelps
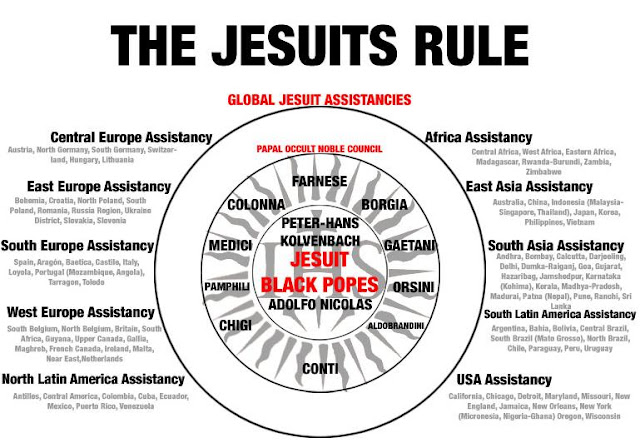
Today the Jesuit Order has about 19,000 members. Of the about 13,500 priest members, some have taken the 4th vow secret oath in which killing a ‘heretic’ is not considered a crime. The ranks of Jesuits are thinning; From 36,000 members at the order’s zenith in the mid-1960’s, to 26,000 in 1983, to 23,000 in 1995 [10]. The Jesuits are geographically organized by 91 provinces (61?), which each belong to one of 10 assistancies around the world.
The Military Order of Malta has about 12.500 members (excluding volunteers), and Opus Dei has about 26,000 celibate members (excluding volunteers).
The Vatican-Jesuit-Masonic crusades, up to our present time, show their criminal “full-spectrum dominance” doctrine is effectuated all over the world by:
The Vatican-Jesuit-Masonic network operates mainly out of the following cities:
_____________________________________________________________
The Black Pope
Anyone who can not see that the Catholic Church dominates
American Politics needs to look at these photographs.
But God hath chosen the foolish things of the world to confound the wise; and God hath chosen the weak things of the world to confound the things which are mighty;
And base things of the world, and things which are despised, hath God chosen, yea, and things which are not, to bring to nought things that are:
That no flesh should glory in his presence.
But of him are ye in Christ Jesus, who of God is made unto us wisdom, and righteousness, and sanctification, and redemption:
That, according as it is written, He that glorieth, let him glory in the Lord. 1
Superior General of the Society of Jesus.
Treasury Secretary under President Nixon. In the private sector, he has become one of America’s 400 richest individuals by working in international finance. Today he is the President of the John M. Olin Foundation, a major funder of right-wing think tanks.
CIA agent, conservative pundit and mass media personality.
William’s brother, head of Radio Free Europe and Radio Liberty.
The grand dame of the Cold War was also a Dame of Malta. She was a popular playwright and the wife of the publishing tycoon Henry Luce, who co founded Time magazine.
CEO of the international division of Chase Manhattan Bank, a Rockefeller institution. (Nelson Rockefeller was also a major CIA figure.)
President, U.S. Steel
Chairman, General Motors
Chairman, Merrill Lynch.
Chairman, Metropolitan Life Insurance Company.
Founder of the Kennedy empire.
Owner, Hilton Hotel chain.
Heir, Schick razor fortune. Frawley is a famous funder of right-wing Catholic causes, such as the Christian Anti-Communist Crusade.
Aerosol magnate.
Executive vice president of Morgan Guaranty Trust.
Chairman of the executive committee of the Emigrant Savings Bank of New York.
President, W.R. Grace Company. He was a key figure in Operation Paperclip, which brought Nazi scientists and spies to the U.S. Many were war criminals whose atrocities were excused in their service to the CIA.
Of Saxe, Bacon and Bolan, the law firm of Senator McCarthy’s deceased aide Roy Cohn.
Baseball Commissioner
Extreme right-wing leader among American Catholics, and fervent abortion opponent.
The “American Pope” was at one time the most powerful Catholic in America, an arch-conservative and a rabid anti-communist.
One of the highest-ranking conservatives in the American church.
Secretary of State under President Reagan.
dmiral James D. Watkins
Hard-line chief of naval operations under President Reagan.
Senator (R–Al).
Senator (R-New Mexico).
Governor of Alaska and secretary of the interior.
It was only a matter of time before other nations caught on to these fronts. They learned that when the CIA comes to their countries to commit their crimes and atrocities, they come disguised as American journalists, businessmen, missionaries and charity volunteers. Unfortunately, foreigners are now targeting these professions as hostile. In Lebanon, terrorists held U.S. journalist Terry Anderson hostage for nearly seven years, on the not unreasonable assumption that he was a spy. Whether or not this was true is beside the point. The CIA has put all Americans abroad at risk, whether they are CIA agents or not. In hearings before the Senate in 1996, many organizations urged Congress to stop using their professions as CIA cover. Don Argue of the National Association of Evangelicals testified: “Such use of missionary agents for covert activities by the CIA would be unethical and immoral.”
Mel Gibson’s first name comes from a 5th-century Irish saint, Mel, founder of the diocese of Ardagh containing most of his mother’s native county, while his second name, Columcille is also linked to an Irish saint. Columcille is the name of the parish in County Longford where Anne Reilly was born and raised.
Mark Wahlberg
Has A Mark Vatican Cross In His Bedroom
- Viet Dinh Professor of Law Georgetown University
And the powerful Roman catholic, Fascist, former president of Spain, and personal friend of King Juan Carlos of Spain, José María Aznar is current President (of the board of directors). He is the one Hugo Chavez called a Fascist and King Juan Carlos told Hugo to “shut up”.
- Aznar’s government, along with the Bush administration, openly backed the April 2002 military coup against Chavez (Which probably had several psychological functions on the nations involved because Hugo Chavez is one of them as far as I know. See pics on this page.)
- Aznar actively participated in the “illegal” and brutal invasion of Iraq, on the basis of false assertions about weapons of mass destruction.
Director of Rothschild Investment Trust Capital Partners plc since 1997
Holy Cross student
University Student
Interesting Fact: James Carville who accredited for getting Clinton elected president married someone who was instrumental in getting George HW Bush elected.
July 09, 2008
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wMxhmdWSuA4
Minister Louis Farrakhan is currently the leader of a reconstituted Nation of Islam, the original organization having been renamed and eventually dissolved by Warith Deen Muhammad. The Nation of Islam’s National Center and headquarters is located in Chicago, Illinois and houses its flagship Mosque No. 2, Mosque Maryam in dedication to Mary, mother of Jesus.




Jesuit Trained William (Bill) Clinton who is supposed to be Baptist
(maybe he means to say Papist) receives of the heretical ‘holy eucharist’.
Jesuit Trained, Liberal democrat, pro-abortion, Skull and Bones member John Forbes Kerry
receives heretical ‘holy eucharist’ which only devout practicing Catholics may partake of.
(Where a priest makes a mark of a cross in ashes on their foreheads.)




Under Reagan’s presidency official diplomatic ties were reestablished between the Vatican and the U.S. they were broken in 1865 after President Lincoln’s assassination and for orchestrating the Civil War!!





Senator McCarthy hat he use this issue in order to gain political prominence.
Walsh vigorously promoted anti-Communist thought throughout his career.

been easy to manipulate at the hands of Jesuit Edmund Walsh who suggested to
McCarthy that he could make a name for himself by taking an extreme anti-communist
stance thus coining the term McCarthyism which also ended up with the Senators
total downfall.
Former Governor of Florida, Jeb Bush, meeting with Pope Benedict
Montini [a.k.a “pope” Paul VI] pictured giving a speech on October 4, 1965
at the United Nations Montini in his address to the United Nations, called
that godless monstrosity [The UN] “the last, best hope of mankind…” (Below)
of the Society of Jesus, the largest religious order of the Roman Catholic Church.
progressive theologian Karl Rahner SJ.(Society of Jesus)
After the Belgian detailed his Big Bang theory, Einstein stood up applauded, and said, This is the most beautiful and satisfactory explanation of creation to which I have ever listened. Lemaitres theory, the idea that there was a burst of fireworks which marked the beginning of time and space on a day without yesterday, was a radical departure from prevailing scientific understandings, though it has since come to be the most probable explanation for the origin of the universe. (In other words, a Jesuit was behind the embarrassing doctrine of the “Big Bang” theory. -TR )
The History of The Society of Jesus in Malta – Our Presence, Houses and ApostolatesBy John Scicluna, S.J.
- The Beginnings
- Expansion
- Suppression
- Restoration and Growth
- Jesuit Refugees
- Seminary and Colleges
- An end and a new beginning
- Separation and new spring
- The Houses
- Other projects
- Apostolates
- Media
- Youth
- Collaborators
- Some Recent Events…
The Beginnings
Already in St. Ignatius’ time, from 1553, the bishop of Malta, Dominic Cubelles, began repeatedly asking Ignatius Loyola, the founder of the new Order, the Society of Jesuits, also known as Jesuits, to send some members to Malta so as to help reform the diocese and the ruling Hospitalier Order of St John (Knights of Malta), as well as to start a College.
Ignatius saw the possibility of using Malta as a base to send Jesuits to Girba, near Tripoli. Given Malta’s geographic position and the proximity ofthe Maltese language to Arabic, Malta seemed to Ignatius an ideal stepping stone to train missionaries for the Muslim world.
In 1554, St Ignatius planned to send Fr Nicholas Bobadillia to carry out the diocesan apostolate and other Jesuits to open the College. Due to quarrels between the Bishop and the Order, however, the plan did not materialise.
In 1565 the newly elected Fr General, Francis Borgia, sent a group of Jesuits with the army that was put together to relieve Malta from theGreat Siege. It is not known if they actually landed, and none further is known on this second attempt.
The first known Jesuit to come to Malta was Fr G. Carminata, a well known preacher. In 1577, he was invited by the Grandmaster to give Lenten sermons to the knights of St John.
The first Maltese to join the Jesuits was Rev. Simon Bonnici, a diocesan priest. He entered the noviciate in Rome in 1578 and died in 1589.
The newly appointed bishop of Malta, Thomas Gargallo, in 1578, asked Fr Carminata, then provincial of Sicily, tosend Jesuits to Malta to open a College. Fr Carminata obliged by sending three: Fr Casati, Fr Paraninfo and Br Longo. However, due to disputes between the Maltese authorities, the college was not built, and the three Jesuits were recalled back to Sicily.
↑ Back To Top
Expansion
The Sicilian Jesuits returned to Malta in 1590, on the bishop’s insistence, and settled helping victims of the plaguethen ravishing the islands.
In March, 1592, Pope Clement VIII sent letters to the bishop and Grandmaster ordering them to settle any differences at once and provide funds for the establishment of a Jesuit college. The college was founded instead of a seminary, the setting up of which was ordered by the Council of Trent, and confirmed in a 1591 diocesan synod. Two Jesuits arrived to make the necessary preparations.
The College opened on 8th March 1593 in a house in Valletta which served both as the school and the residence for nine Jesuits. The construction of the “Collegium Melitense” (which until the 1970’s housed the Malta University) andthe Jesuit Church in Valletta, started in 1595. Within two years, the Jesuits had already moved into the new building. Besides teaching within the college, the members of the Jesuit community distributed food to the poor, heard confessions, preached in the villages, taught Christian doctrine to children, worked for conversion of Turks, acted as intermediaries between rival families helping to resolve blood feuds, and established Marian congregations for different groups of people.
On two occasions the Jesuits were made scapegoats and had to leave Malta. The first occasion was in 1639 when tensions arose between the rigid and orthodox Grandmaster and a number of liberal knights. The knights used theJesuits as a scapegoat: after several threats, the Jesuits were forced to leave. On intervention by the Pope, thesituation promptly returned to normal, and the Jesuits were back by September, to reopen the College in December.
The second occasion was in 1768. After the Jesuits were expelled from different countries in Europe, it was the turn of Malta to expel the Jesuits. At the end of April, 1768, Grandmaster Pinto – who himself appreciated the work ofthe Jesuits in Malta – banished the Order from Malta, and consequently, against the Pope’s wish, confiscated all its property. The Jesuits were put on a French ship and taken to a port near Rome.
↑ Back To Top
Suppression
The rulers of Europe, forced the Pope, on threat of schism, to ban the Jesuit Order. The Jesuits, who had considerable influence on all parts of society through their colleges, itinerant preaching, spiritual direction and were regarded as obstacles in the rise of absolute monarchies and opponents of the illuminist culture. On 21st July, 1773, Pope Clement XIV, issued an administrative decree by which he suppressed the Society of Jesus.
The decree was forwarded to the bishops to be communicated by them to the Jesuits resident in their dioceses. In most of the countries of Europe the decree of suppression was carried out to the letter, the Jesuits as a body submitting loyally to the decision of the Pope.
However, Catherine II of Russia and Frederick II of Prussia were impressed so favourably by the work of the Jesuits as educators that they forbade the bishops to publish the decree in their territories. Thus, providentially, theSociety of Jesus continued to exist in White Russia and Prussia. In the other countries many of the Jesuits laboured as secular priests, others of them united in different congregations.
Gradually, Clement’s successors in 1778 allowed the Jesuits to open a noviciate in Russia, a community of former Jesuits in England at Stonyhurst in 1803 was allowed to affiliate with the Jesuits in Russia the following year theSociety was re-established in Naples. In 1797, the duke of Parma, with the encouragement of Joseph, received permission from the pontiff to establish a Jesuit province in his duchy. Then the Pope allowed the Order to be restored in Naples. Schools and a college were opened in Sicily.
↑ Back To Top
Restoration and Growth
After several pleas from Bishops and Catholics worldwide, one of the first things that Pope Pius VII did after returning from Napoleonic exile to Rome was that on 7th August, 1814, almost exactly forty-one years to theday since Clement XIV suppressed the Society, he issued the Bull, Sollicitudo omnium Ecclesiarum formally re-establishing the Society.
In short time, from the few old Jesuits that remained, the Order grew and spread at an immense rate. Many of the works established before suppression, not since taken up by other orders, were revived, and a number of new ones were added to these, most of which were based in countries where Catholics were a mere minority.
After the re-establishment of the Order, the first Jesuits returned to Malta in 1839 but stayed only for a few days while in transit to other countries. At this period, Malta was a British colony, and the Maltese started to put pressure on the authorities to set up a Jesuit college in Malta once more. The government not onlydisagreed, but in 1846 set up a Protestant college that was doomed to close soon as the sons of the Maltese intelligentsia, for whomthe college was aimed, ended up in the Jesuit college in Noto, Sicily.
Many Maltese, worried about the strong Protestant influence brought about by the British presence, petitionedPope Clement XVI to intervene. The Holy Father asked the Jesuit General, who in turn asked the Provincial in England, to open a College in Malta. a The government yielded to the opening of a Jesuit college in Malta, provided it was run by British citizens. In 1845, English Jesuits founded St Paul’s College in Mdina. This closed down in 1852 and after a brief restart in Valletta, the college shut its doors permanently in 1858.
↑ Back To Top
Jesuit Refugees
In 1848 and during the wars of Italian reunification (1860), the Jesuits in Naples and Sicily were threatened with expulsion, and many ended up in Malta. The Bishop welcomed the Jesuit refugees and gave them lodging in part of San Calcidonio in Floriana. (San Calcidonio, also known as Our Lady of Manresa Retreat House, was opened by Fr Pier Francesco Rosignoli, SJ, in 1753 and closed in 1768 after the Jesuits’ expulsion when it fell into the hands of theDiocese of Malta. It may be mentioned that when the Jesuit returned in 1860, they remained in residence at Floriana till 1918. Between 1860 and 1867, the Provincial Curia of the Sicilian Province was house in this Residence. From 1858 to 1910 and again from 1921 till 1977 the diocesan seminary was housed here. Now it is occupied by theArchbishop’s Curia.
But San Calcidonio did not have enough room for all the Jesuit refugees, so some of them shifted to a large house near Annunciation Street, Hamrun. Later they moved to another house at Santa Venera, where the present Carmelite Priory is situated.
In 1867 a noviciate was opened in Gozo. In 1872 a large house in Lija was acquired to accommodate Jesuits from theFrench, Neapolitan and Sicilian Provinces.
In 1877, the noviciate was transferred from Gozo to Santa Venera, and in 1879 from Santa Venera to Notabile. In 1881, the Palazzo Parisio in Naxxar was rented to house the increasing number of Sicilian and Maltese young Jesuit Students in the Juniorate, philosophate and theologate. San Luigi Gonzaga was chosen as the patron Saint of this new house of studies in Naxxar.
But the Jesuits were not content with the transfer of residences and the make-shift accommodation of their young students. They wanted to build a large college, suitable and comfortable, that would take in all Jesuit students under one roof. The site chosen was at Mriehel in Birkirkara. The college was constructed with the funds acquired from the sale of the Sainte Pulcherie in Constantinople which belonged to the Sicilian Province. Once again the new College, which opened in January 1897, was also called Collegio San Luigi.
↑ Back To Top
Seminary and Colleges
The diocese of Gozo was established in 1864 and the following year the Bishop asked the Jesuits to open, take overthe direction of and staff the Major Seminary and the secondary school which had to be opened. The seminary and school opened in October 1866 and was staffed by Fathers from the Sicilian Province. The students came from Malta and Gozo as well as from Sicily. But in 1903 difficulties started hitting the Seminary Jesuits hard. Efforts were made to resolve the difficulties and in August, 1909, after having run the Seminary and given their best to theGozitan clergy and people for a span of 43 years, the Jesuits left unceremoniously.
In 1876 several Maltese families petitioned Pope Pius IX to open a Jesuit College in Malta. The request was passed on to the Jesuit General who agreed and in turn sent it to the English Provincial who also agreed to open thecollege.St Ignatius College at St Julian’s opened in 1877 in the building which was used by the Malta Protestant College which closed down in 1865 and bought by three Maltese gentlemen. The new College adopted the English system of education with English as its medium of instruction. A church adjoining the College was completed in 1881. The College flourished with good academic results and came to be recognised as one of the leading schools.The Jesuits also involved themselves in various pastoral ministries especially among the members of the English communities and the Military.
Due to trouble from external forces, it was decided to close down St Ignatius College. The official reason was thatthe Bishops in England were asking the Jesuits to open a College in Leeds. The College closed down in July, 1907.
In the meantime, the political atmosphere in Sicily became sufficiently safe to justify the transfer in 1906 the Jesuit students to Acireale, and to Bagheria near Palermo. After their return to Sicily the Jesuits were planning to implement the promised to open a college at Palermo. But …
↑ Back To Top
An end and a new beginning
Thus the building of the Collegio San Luigi in Birkirkara was left vacant and open for sale.
When news about the possible closure of St Ignatius’ College began to circulate, many Maltese to Fr General, to theEnglish Provincial and to the Pope to avoid such a decision. But at the beginning of 1907 the parents were informed that the College would close down in July 1907. The parents were worried and over three hundred parents signed a petition to Pope Pius X to intervene. The Pope passed on the request to Fr General who asked the Sicilian Provincial to postpone the opening of the college at Palermo and open the desired College at Birkirkara.
In the beginning of summer 1907, the Provincial appointed Fr Emmanuel Grima, then the Rector at the Gozo Seminary, to prepare in three months for the opening of a College in the existing building of Collegio San Luigi. Most of the furniture, including the statue of the College Madonna were brought over from St Ignatius’ College.Thenew College at Birkirkara under the protection of St Aloysius opened on 8th October, 1907.
↑ Back To Top
Separation and new spring
At the turn of the 20th century there were three Jesuit communities in theMaltese islands, at the Seminary at Gozo (till 1909), and in Malta at San Calcedonio (till 1918) and the College. These, together with Greece, formed part of the Sicilian Jesuit Province. In 1924, a second community was opened at Floriana when the Jesuits were entrusted by theGovernment with the administration of Sarria church, Floriana, with theadjoining residence, both government properties.
This link with Sicily continued until 7th September, 1940, when, through a telegram, Fr J. Delia, the College Rector, was informed that he is appointed as Fr General’s “Delegate for the administration of the College, thus effectively separating the two Jesuit communities from the Sicilian Province and made them directly dependent on him.
At the end of the War the Jesuit Vicar General asked Fr Delia to prepare to open a Noviciate in Malta which was opened on 1st October, 1945.
Shortly after his election of the new Fr General informed Fr Delia about his decision to establish the Vice-Province of Malta. The Decree establishing the Maltese Vice Province was promulgated on 29th June, 1947. A few days later Fr Delia was appointed the first Vice Provincial. In 1983, the Vice-Province became a full-fledged Province.
The return of the Maltese Fathers, Scholastics and Brothers from Italy and the entrance of young men in thenoviciate heralded a new bright future for the Jesuits in Malta. Existing apostolates and works were strengthened and new openings were being planned.
↑ Back To Top
The Houses
– St. Aloysius’ College, Birkirkara
The College, inspired by Ignatian spirituality, imparts a holistic education. Through spiritual, cultural and social work experiences the College aims to enable the students to be persons for and with others.
Seven years after the opening of the College as a Secondary school, in 1914 a church was built and in 1928 a theatre hall was inaugurated. The Scouts at the College were established in 1916.
At the beginning of World War Two an attempt to confiscate the College was successfully overcome. Then duringthe War almost half the College was used as a hospital. For some time the Bishop’s Curia and other church and health department offices were located here. Medical students and seminarians had their classes here.
After the establishment of the Vice-Province, the Provincial’s Offices were at the College till 1950 when they moved to Floriana.
The fields opposite the College were bought in 1947 for a new playground which was inaugurated in 1954. That same year the College badge and uniform were changed. The CYLO was started in 1960. Then in 1962 the Sixth Form opened, only with an Arts section and suspended four years later. After four years it was reopened with theaddition of two other sections: Languages and Maths. In 1972, girls were admitted in the Sixth Form. A new Complex for the Sixth Form was built and inaugurated in 1991.
The boarding system was abolished in 1963 and the day-boarding system finished in 1979. The College PTA and theCollege Newsletter were started in 1969.
The Church Schools caused by the government problem started in 1979 and dragged on for five years. First there was the issue of the pupil-worker scheme and the capitation fees were stopped. The next move was that the fees were frozen and then fees could not be charged. However, the parents voluntarily made donations. Big protest rallies were organised by the PTAs and Former Students. The Government withdrew the schools’ licence and classes were held in parents’ homes. At one time the Police placed chains on the College gates but the Parents and Old Aloysians stayed on to guard the College and the community. In November 1984, after an agreement between theGovernment and the Archbishop the Schools re-opened.
In the College church, Masses for the public are celebrated daily and it is often a preferred venue for weddings.
The College Sports Complex and Gym was opened in 1997. The Jesuit residence was completed in 2002. During theCollege Centenary Year in 2007 the weekly holiday was shifted to Saturday. In October Fr General Peter-Hans Kolvenbach presided over the Centenary celebrations.
Another milestone in the College annals opened in June 2008 when the Jesuits took over Stella Maris School run bythe nuns to serve as the Primary Section of the College.
The JRS (Malta) offices are housed in the College Gym.
Over the span of a century the College contributed in no small way to Maltese society and to the formation of many important Maltese personalities attended the college, including Presidents of the Republic, noteworthy politicians, priests, religious, artists, lawyers, journalists and scientists.
– Sarria Residence, Floriana
This residence was opened in 1924 when the Government entrusted the Jesuits with the administration of thechurch, which was built in 1677 by Martino de Sarria, a knight of St John.
Throughout the years, due to its central location, the church it used for various religious meetings. One was by theM– USEUM Society and its founder, Dun (Saint) Ġorġ Preca used to address the weekly meetintg of the members.
More than twenty different groups meet here every month. On weekdays, a Mass is celebrated for workers fromthe nearby various government offices. On Sunday a Mass in English is celebrated.
The “Teenagers Correspondence Club” was established here and was followed in 1964, by the “Teens and Twenties Trust” (4Ts) which started here. The “Friendship Groups” saw their beginnings here in 1972.
Between 1950 and 1962, the Provincial’s Offices were located here.
– Loyola House, Naxxar
The Jesuit Noviciate opened on 1st October, 1945, in a Villa belonging to Marquis John Scicluna who in 1950 then donated it to the Province, was, for many years, the cradle of the Province where young men who decided to follow Christ began their spiritual journey
In 1952 the foundation stone for the new noviciate and juniorate building was laid. With the dwindling number of novices, it was decided, in 1971, to give part of the new building to the Little Sisters of the Poor for an Old People’s Home. Due to lack of vocations, the Sisters withdrew in 1992 and the Catholic Action began to run it.
The first floor of the old building was renovated in 1995 and called “Monserrat” to be used by the Vocations Team and other youth groups for meetings and live-ins.
The Province Infirmary is also housed here.
From 1975, the Provincial’s Office are in a section of the House.
The Sanctuary dedicated to Our Lady of the Way forms part of the House. Every day a number of Masses are celebrated and throughout the day many persons come here to celebrate the Sacrament of Reconciliation.
Various Fathers of the community give pastoral service in the parish and elsewhere.
– Manresa Retreat House, Victoria, Gozo
After 43 years’ service at the Bishop’s Seminary in Gozo, the Jesuits left theIsland. After a lapse of 44 years, at the request of the Bishop of Gozo, the Society was entrusted with the administration of the Retreat House for the retreat apostolate and spiritual help to the faithful of the neighbourhood. It opened on 21st October, 1953.
The House was extensively refurbished in 1995 and it is very much sought after by priests, religious and lay persons from Gozo, Malta and abroad, for directed, preached or private retreats, meetings, seminars and for some rest in quiet surroundings.
In the church, which forms part of the House, Masses are celebrated daily forthe public.
– St Philip’s Residence, Senglea
This was the next Residence to be opened. The Archdiocese and the Collegiate Chapter of the city entrusted the Church and Residence to the Jesuits. It was opened on 1st November, 1957.
The church, dedicated to Our Lady of Good Havens (the Visitation), was built in 1640. It is known as the church of St. Philip Neri as it was given to the Oratorians who rebuilt it in 1741. When the Oratorians left Malta, the archpriest of Senglea became responsible for the church. During the cholera epidemic the friary adjacent to the church served as a hospital.
During their stay at Senglea, the Jesuits carried their pastoral ministry in the church, assisted the Archpriest and helped in the nearby parishes. Many people always found some priest available to help them in their spiritual and material needs.
At the end of 1997, Fr General issued a Decree which “suppressed and dissolved” the community. At the end of March, 2008, the Jesuits handed the keys to the Archdiocese who passed them on to the Salesians.
Two months later, the Archpriest organised a Thanksgiving Mass for the dedicated service the Jesuits gave at Senglea.
– Xavier House, Valletta
In the 19th century this building was a hotel and later leased out to various families. A benefactor of the Province donated this vacant building to the Province. In September, 1962, the community moved in. At the same time theProvincial’s Offices were also shifted here from Floriana.
This Residence who just opposite the building of the University of Malta (initially the Jesuit’s Collegium Melitense) which some years later shifted to Msida.
In 1965, during the time of Vatican II, John XXIII Librarty was started here. Many students, priests, male and female religious and other lay persons availed themselves of the services it offered.
The office of the Benefactors Association is located here.
For a number of years the editorial office of the magazine Problemi ta’ llum and Regina et Mater were also in this House.
Everyday, some members of the community celebrate Mass in the Jesuits church (now government property). TheFathers are also available for confessions and spiritual direction.
– Mount St Joseph Retreat House, Mosta
In 1753 the Jesuits had built the Retreat House at Floriana which after their expulsion became diocesan property. When the Jesuits left San Calcidonio in 1918 there was no retreat house in Malta. The need for a Jesuit retreat house in Malta was keenly felt by the Province and the Archbishop.
In 1961, on the outskirts of Mosta town, a property was bought in an area known as San Ġużepp tat-Tarġa (because of St Joseph’s statue on steps leading to the plain below). Construction work started in early 1961
and inaugurated in December, 1964. Our Jesuit Brothers played a big part in procuring the materials for theconstruction and in other works.
The House was extensively refurbished and re-opened in December 2005. The huge concrete statute of St Joseph onthe façade of the House developed cracks. It was replaced by another exact replica in fibreglass.
The Retreat House is located in spacious and quiet surroundings with an enchanting wide view of the plain belowand the blue sea in the distance. This is one of the reasons why many individuals and groups throughout the year seek this place for encountering the Lord. Others come here to participate in some course, seminar or live-in.
The Fathers in the community are always available to welcome and assist those who come for some spiritual nourishment and refreshment. The priests also assist in various parishes.
– Villa Pacis, Bugibba
In 1962 construction work started in a quiet area at Bugibba, St Paul’s Bay for a summer residence and for retreats during the other months. It was inaugurated in the summer of 1963. However, after a few years it was surrounded by a cluster of buildings which mushroomed in a short time. Thus the Province was forced to sell the house in 1969.
↑ Back To Top
Other projects
In 1957 land was bought at Blata l-Bajda on the way to Valletta for a National Shrine in honour of the Sacred Heart together with a residence for the staff and offices of the Apostleship of Prayer, the Christian Life Community andthe Young Christian Workers. After Fr General asked to postpone this project, the land was sold in 1964.
With the approval of the Archbishop, Fr General approves the proposal to buy land in the region of “Savoy Hill”, Sliema, for a church and other apostolic works. Later Fr General approves the plans for a Residence and church here.
After a detailed study, in 1960 Fr General asks the Province to postpone the project at Blata l-Bajda and to abandonthe Savoy Hill plan. Instead he suggests that it would be better to plan for a Retreat House and a new College.
Later he agreed with the Province to postpone opening a College at Ta’ Giorni, St Julians, in a property donated tothe Province but advises to retain the property. Later in 1968 he approved the sale of the property and with theproceeds establish a Scholarship Fund at the College and pay off outstanding debts of other projects.
A house at Oxford was rented and opened in 1957 for Maltese Fathers and Scholastics studying at Oxford University. Then in 1965 it was later leased out and in 1972 it was sold and another house in London was acquired. It was sold in 1995.
– Dar Manwel Magri SJ, Msida
The Collegium Melitense, later the University of Malta, started at Valletta in 1592. Then in 1968, the University shifted to Msida. At the end of 1968, the Province acquired a small plot of land near the main gate of the new university for a new Jesuit residence. In December, 1992, the first community settled in the new Residence named after Fr Manwel Magri, SJ, a Maltese ethnographer, archaeologist and writer.
Close to the Residence is the University Chapel. In 1971 a Jesuit was officially appointed the first full time Chaplain at the University. But when the University was still at Valletta Jesuit Fathers used to attend to the needs of thestudents.
The Jesuit Chaplain, assisted by other Jesuits, lay staff and volunteers, cater for a population of over 10,000 comprising Professors, other staff and students. The Chaplaincy organises various religious and cultural activities. During the summer months the inYgo Youth Network and the Chaplaincy organise voluntary work in Malta and in other countries. Long term voluntary service abroad has been launched.
The House is a venue for various meetings organised by the Jesuits and used by groups for their meetings.
– Fekruna Rest House
Two adjoining houses at St Paul’s Bay were acquired in 1980 to serve as a rest house for Jesuits. It is also used for meetings of apostolic sectors of the Province and by youth and CLC groups for live-ins.
– Marina Road, Pietà
In 1973, due to shortage of accommodation at the College, some Fathers took up Residence in a rented house on Birkirkara Hill, St. Julians. Then in 1975, it was closed and the community moved to another rented house at Marina Road, Pietà.
– Dar Pedro Arrupe, Zejtun
This is the last House that was opened in the Province. The presence of theChurch and of the Jesuits in the south of Malta was lacking. So in 1989, this Residence was started which houses the Jesuit Centre for Faith and Justice Centre.
The mission of the Centre is to link the service of the Christian faith withthe promotion of social justice, to disseminate Gospel values and thesocial teachings of the Church, to train and form influential agents towards Christian social commitment, and to ensure presence, insertion and involvement among the grassroots. It works to support activities aimed at promoting social justice, to reflect on, raise consciousness and seek solutions to social problems and injustice in the light of the Christian faith.
The Formation/Reflection branch, made up mostly of non-Jesuits, organises and runs courses, focus groups, spiritual exercises with a social theme, public lectures, contributions to the media and at times action on a specific issue involving social justice. It reflects on current issues and receives ongoing formation.
Members of the Insertion branch (the Jesuit community living at Zejtun) ensure Jesuit presence, witness and contact with the grassroots as a way of empowering them and integrate their experience in their reflection and action in promoting social justice.
The Centre has already shown practical commitment in favour of asylum seekers and refugees. Migration, and its darker dimensions of racism and xenophobia, is one of the priority areas of the whole Society of Jesus. Together with the Jesuit Refugee Service, both on the local and the European level, it has also participated in international initiatives.
As part of the Centre, in January, 2001, the Paulo Freire Institute was opened at Zejtun for the promotion of literacy and community development. It aims to encourage children to improve their reading and writing skills. It is also vital to empower their parents with important skills. Thus the main activities presently carried out at the Institute are: Non-Formal Educational Activities for children; Literacy Project for children; Literacy for Employment Project; Parental skills programmes; Female empowerment courses; Community Social Work and Energy-conservation educational programme.
The priests in the community, besides helping in parish, on Sundays they celebrate Mass at the Refugee Detention Centres.
↑ Back To Top
Apostolates
– International Apostolates
The mission of the Society of Jesus is indeed a universal one, without any kind of frontiers. According to theFormula of the Institute, a Jesuit is one who desires to serve as a soldier of God beneath the banner of the cross to serve the Lord alone and the Church, his spouse, under the Roman Pontiff, the vicar of Christ on earth. Thus theJesuits consider themselves as servants of Christ’s mission. Concretely its aim is the defence and proclamation ofthe faith, which leads us to discover new horizons and to reach new social, cultural and religious frontiers.
Long before the Maltese Province was established always lived this awareness of sharing in the universal mission of the whole body. Individual Jesuits served in Tunis, in Canada and British Guyana.
The major missionary enterprise in the history of our Province is surely the beginning of the mission in India among the Santal tribals. The seed sown there in 1925 has grown into a sturdy tree and given fruit. The Santal Mission has developed. Today the territory has been divided into three dioceses which are co-extensive with Dumka-Raiganj Province, one of the many Jesuit Provinces in India, with its own noviciate, colleges and other centres.
Maltese Jesuits also served in Vatican Dicasteries in Rome, as well as in the Jesuit headquarters, as Directors of theCentre for Ignatian Spirituality, in the office of the General Treasurer, in the Christian Life Community office and inthe Historical Institute. Maltese Jesuits also serve in the international ecclesiastical Jesuit institutions. With dedication and zeal they also rendered apostolic service in China, the Philippines, Japan, Australia, Sri Lanka, Egypt, Uganda, Kenya, Libya, Ethiopia, Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Lebanon, Israel, Italy, Albania, Romania, France, United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Canada and the United States.
– National
At some time some Maltese Jesuits served the Holy Father in the Apostolic Nunciature in the Archbishop’s Curia asthe Archbishop’s Delegate for Religious, in the Workers’ Secretariat, for Youth in the Secretariat for Education, Ecclesiastical Assistant for the Catholic Action Movement, National Chaplain for the German-speaking community, as Public Relations Officer, as President of the Historical Commission for Causes of Saints and as Judges in theMetropolitan and Regional Ecclesiastical Tribunals. Worth mentioning is that in 1940, the Archbishop appointed one Maltese Jesuit as the Superior of the Missionary Society of St Paul until in 1948 one of the members was elected Superior General.
– Spiritual
From the time of its foundation, the main spiritual ministries have always been preaching the Word of God, administering the sacraments, giving the Spiritual Exercises to individuals or groups, and spiritual direction. Other means of their spiritual apostolates were the founding and animating the Sodalities of Our Lady (today known as Christian Life Community), the Eucharistic Crusade and the Apostleship of Prayer. During Lent the Fathers preach Lenten Sermons in different parishes and groups.
Before and after the War, during the summer holidays, the Province organises retreats for youth.
Regularly the Fathers help in various parishes where they celebrate Masses and in hearing confessions. Some Fathers carried our pastoral work in the Dockyard and in Industrial Estates. For 33 years one Father served as theChaplain of the German-speaking community in Malta. A number of Fathers are involved in Prayer Groups and youth groups. Jesuit Fathers also serve as Chaplains in State and Church schools.
The Sacred Heart of Jesus had entrusted to the Jesuit Fathers to promote and spread the devotion to his heart. TheSociety accepted this “sweet mandate”. Accordingly, through the Apostleship of Prayer with the monthly intentions proposed by the Holy Father, through the Consecration of Families and Groups to the Sacred Heart and through theperiodical Il-Messaġġier tal-Qalb ta’ Ġesú as well as through radio programmes it continues to fulfil its mandate.
In October, 1927, the Director of the Apostleship of Prayer began to organise the corege in honour of Christ theKing.
In the Maltese Province, the Centre for Ignatian Spirituality was established. It organises three-year courses to train lay persons to direct the Spiritual Exercises and be qualified as spiritual guides. An offshoot of this Course has been the establishing of the “Parish Ignatian Ministry”.
– Diocesan Clergy Formation
The Maltese Jesuits have made a significant contribution to the formation of the diocesan clergy. In Malta, in theArchbishop’s Seminary, except for two years, from 1934 to 1988, the Spiritual Father was a Jesuit. Afterwards there were Assistant Spiritual Fathers. Other Jesuits were involved in lecturing in the Faculty of Theology at theUniversity.
When, between 1978 to 1988, the Faculty of Theology at the University of Malta was suppressed, and the Holy See established a Pontifical Faculty at the Seminary, a Jesuit Father was elected President of the Faculty.
After the Diocese of Gozo was established, in 1866 the Jesuits were invited to take over the direction and staffing of Bishop’s Seminary. This continued till 1908. Then in 1970, the Bishop of Gozo invited the Jesuits to provide a Rector for the Seminary. In 1997 this responsibility was passed on to the diocesan clergy.
Other Maltese Jesuits worked in Seminaries in Kenya and Sudan.
– Chaplaincy at the University
When the University of Malta was still at Valletta, various Jesuits used to attend to the spiritual needs of thestudents. After the University in 1968, moved to Msida, in January, 1971, a Jesuit was officially appointed the first full time Chaplain.
The Archbishop of Malta donated funds for the building of St Thomas More chapel where there are the offices ofthe Chaplain, his assistants and staff.
After teaching Religion at the Junior College for some years, a Jesuit was appointed as Spiritual Father there in 1984, But the following year the government stopped the ministry he had been rendering for the past seven years. After a petition by more than a hundred staff members and by over one thousand students, the Education Minister refused to re-consider his decision. He was re-appointed in 1988 and continued till 1998. He was succeeded by another Jesuit till 2004.
– Intellectual apostolate
In 1961, for the first time since the Society lost the University during the Suppression, a Jesuit was appointed Lecturer in the Faculty of Philosophy at the University, and continued till 1964. Then in 1965 Fr Maurice Eminyan was appointed part-time Lecturer of Dogmatic Theology and Ecumenical Theology at the University and in 1968 he was elected Dean of the Faculty of Theology.
When the Foundation for Theological Studies was founded in 1990, Fr M. Eminyan was appointed its first Director.
In subsequent years other Jesuit Fathers were appointed Lecturers in the Departments of Biology, of Psychology, of Spiritual Theology, of Moral Theology, of Church History, of Law, of Spirituality and Pastoral Psychology, of Philosophy and of Latin and Greek.
Other Maltese Jesuits also fulfilled their intellectual apostolate abroad. One Father lectured at Nairobi University, another at the Oriental Institute in Rome. At the Gregorian University they lectured in the Departments ofTheology, Philosophy and Church History. Another Father lectured in the Theological Faculty at Naples. One Father was Professor of Theology at the University of Detroit. Two others lectured at Heythrop College of the University of London. One Father lectured in Philosophy at the Pontifical Athenaeum in Pune, India.
In 1968 the Province established the Institute of Religious Studies to provide course in theology.
Besides lecturing some the Fathers in the Intellectual Apostolate also published books and articles related to their specialisation.
– Social Apostolate
Two Maltese Jesuits were involved in the Young Christian Workers movement. Fr Michael Galea found the Żgħażagħ Ħaddiema Nsara in Malta 1948. Another established a branch in the Archdiocese of Calcutta in India. In 1959,the ŻĦNbegan to publish the Il-Ħaddiem newspaper.
Already in 1955, the Province founded the “Catholic Social Guild” and in 1970 the Istitut Edukazzjoni Soċjali.
In April 1967, the Province accepted the Maltese Government’s invitation to provide a Principal, a Deputy Principal and two teachers for St Philip Neri’s School, a correctional home for boys at Santa Venera. This continued till December, 1972, when our services were terminated by mutual accord.
Another major step by the Province was taken in 1989 when it opened a Residence at Żejtun together with theCentre for Faith and Justice. An offshoot of this Centre was the establishment of Paulo Freire Institute in the town.
The Centre has been organises courses about the Social Teaching of the Church. It also organised Conferences and Seminars for which speakers from abroad are invited.
Some Jesuits did some work experience at the Malta Drydocks.
Due to the arrival of asylum seekers and refugees arriving in Malta from Bosnia, Iraq and Sudan, the Province established the Jesuit Refugee Service in the Island. Over the years it has been rendering yeoman service in assisting refugees in their needs, especially through legal assistance by qualified lawyers to legalise their situation especially in applying for refugee status. Social workers also see top their other needs.
↑ Back To Top
Media
The first periodical in Maltese was Il-Messaġġier Malti tal-Qalb ta’ Ġesú which started publication in 1912 and wound up in 1973. After the War, before the opening of the Noviciate and the establishment of the Province, theperiodical Lil Ħbiebna saw the light of day in 1945. Three years later, the Communities of Christian Life began to publish Regina et Mater for is members. In 2005 these the latter magazine were merged.
In keeping with the times, the Province started a social reflection magazine Problemi ta’ llum which ceased publication in 2000 to be replaced two years later by Orbis which for various reasons was also discontinued in 2007.
St Aloysius’ College till recently used to publish its illustrated annual magazine to record the year’s events in thelife of the College.
In 1948, The Maltese Jesuit, an in house monthly newsletter started publication.
A 74-page booklet Books byMaltese Jesuits: a Bibliography was published in 2002. It contains the titles of books and articles in the original language and translations.
Various Jesuits took part in Radio Programmes and when Television was introduced in Malta some Jesuits are invited to take part in regular programmes.
↑ Back To Top
Youth
Through its educational apostolate and its Catholic movements, theJesuits in Malta and Gozo have always played a very important and influential role in the holistic formation of youth. The contact and apostolate with youth increased considerably through the work of theUniversity Chaplaincy.
At the College, the Catholic Young Leaders Organisation (CYLO) was founded in 1960.
Other organisations established for youth were the Teenagers Correspondence Club established in 1963 and then theTeens and Twenties Talent Trust (4Ts) started in 1969.
Then in 2004, the Ignatian Youth Network, inYgo was established as a part of inYgo International. inYgo brings together young people, ages 16-26, who are in touch with Jesuits and Ignatian spirituality through St Aloysius’ College, the University Chaplaincy, Paulo Freire Institute, the Christian Life Communities and the Saturday evening Mass in Sarria Church.
inYgo seeks to accompany young people in their relationship with God, in building community and in their preferential option for the poor.
During the summer holidays inYgo organises voluntary work in Malta and overseas. Recently, long-term volunteer work abroad was launched
↑ Back To Top
Collaborators
Collaboration with the laity has always been a characteristic of Jesuit apostolate. In recent years this Jesuit-Lay and Lay-Jesuit collaboration has been very much stressed and has become one of the aims of our mission as Jesuits.
In 2001 a Jesuit Father was appointed to oversee the formation of our Lay Collaborators. Then once a year, Jesuits and their collaborators come together to pray, reflect and celebrate their collaboration in the one mission of Christ.
↑ Back To Top
Some Recent Events…
In December, 1997, Fr General appointed Fr Alfred Darmanin as the President of the Conference of European Provincials.
The first Jesuit General to visit Malta was Fr Pedro Arrupe in 1973. His successor, Fr Peter-Hans Kolvenbach, paid three visits to Malta: in 1986, in 1997, for the Golden Jubilee of the Province and in October, 2007, three months before his resignation, for the Centenary Celebrations of St Aloysius’ College.
The present General, Fr Adolfo Nicolàs, visited the Province in October, 2009.
In November, 2009, at Siġġiewi, a statue of Fr Ġużé Delia was inaugurated there.
In September, 2010, an inter-Jesuit Conference project was launched in Malta. The Jesuit Conference of Africa and Madagascar (JESAM) sent one Jesuit from Tanzania and the Conference of European Provincials sent one Scholastic from Poland to work with the Jesuit Refugee Service in Malta.